My Django Dev Environment: Virtualenv, pip, git, & PyCharm
Photo by Luca Bravo on Unsplash
How I use virtualenv and pip to manager my python dependencies per project
Even though I've heard how wonderful virtualenv & pip are for managing Django development environments, I didn't think I needed to bother learning it. But one bored day I did. I'm so glad I did. Truth is, it is just as simple and awesome as everyone says it is. And it's been so helpful with all the computer and OS switching I've done lately.
Here is a brief tutorial on how I use virtualenv, pip, git, & PyCharm to manage & develop Inzolo.com. I won't cover installing any of these. See basic instructions for installing virtualenv & pip.
To create a virtualenv that does not use any global site-packages:
1virtualenv --no-site-packages env_inzolo
Then activate your virtualenv:
1source env_inzolo/bin/activate
To get out of your virtualenv:
1deactivate
Tip: many tutorials I have seen would name their environment inzoloenv, but I put `env` first for consistency in tab autocompletion convenience. I was using just env, but the virtualenv you are using will show up on your command line and it is helpful to see which one you have activated if you have multiple projects.
When you first create your virtualenv, you will need to activate it and install all the requirements in that virtualenv for your project:
1pip install django2pip install south
Once you have all your packages installed, create a requirements file:
1pip freeze > requirements.txt
Now, if you're using git, add env_inzolo to your .gitignore file and add
requirements.txt to your repository.
That's it for the set up. Next time your need to recreate your development environment, it will be simple. Just clone your repository and run these commands:
1virtualenv --no-site-packages env_inzolo2source env_inzolo/bin/activate3pip install -r requirements.txt
That's it!
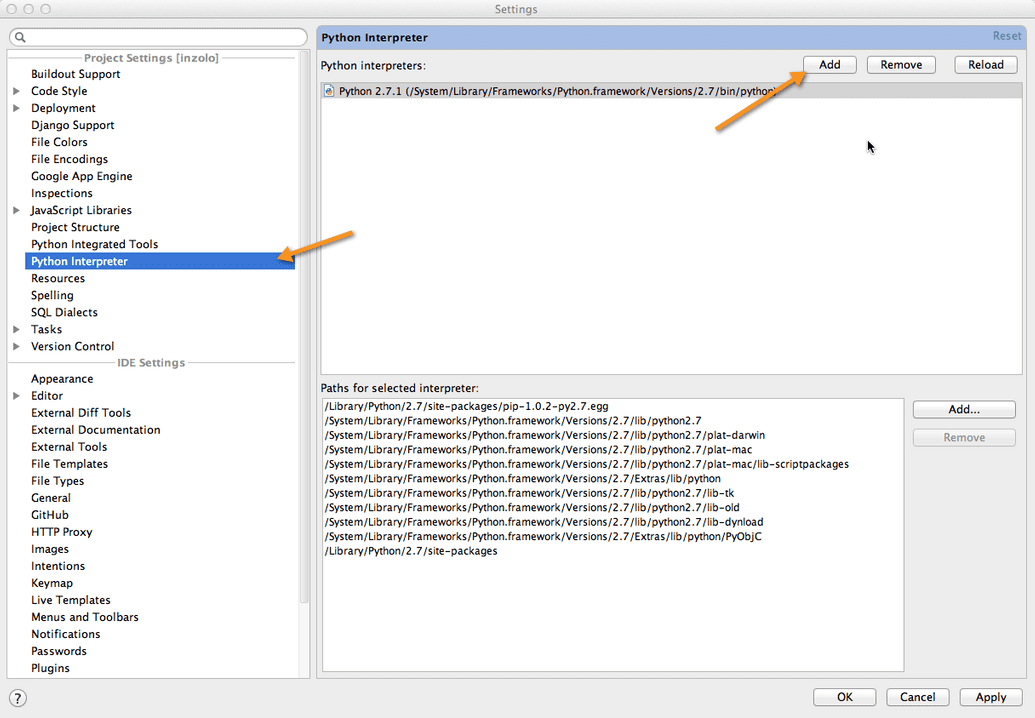
If you use PyCharm you'll want to set up your virtualenv there for your project.
Edit your project settings. Select Python Interpreter -> Add -> Specify Other...
Add python from your virtual_env (env_inzolo/bin/python)
Click Apply to save.
Then click on Django Support and make sure your Django project root, settings file, manage script & template directories are all in order. then you will experience the full goodness of PyCharm!